Project to explore ways to improve fish welfare
A University of Leicester scientist is set to investigate ways to improve the welfare of fish used in scientific research.
Dr William Norton from the University’s Department of Neuroscience aims to test the theory that swabbing has a significantly lower impact on stress-related behaviour and physiology than fin clipping.
“In this project, we will investigate the nature and magnitude of any welfare benefits of swabbing over fin clipping, explained Dr Norton. “Such information is essential to validate the swabbing technique and assure its wider adoption by the growing community of researchers that use fish as laboratory models.”
It is common practice for laboratories to collect DNA samples from fish. It is mostly done to confirm the genetic strain of fish, their population of origin, or whether an individual contains genes that are relevant to the research.
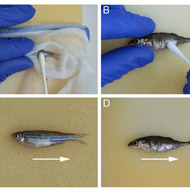
Typically, DNA sampling is performed by fin clipping, an invasive procedure carried out under non-terminal anaesthesia. A recent study found that of the estimated 3,250 zebrafish laboratories worldwide, 85 per cent use fin clipping to collect DNA.
The new technique involves gently stroking a swab (sterile cotton bud) along the flanks of the fish whilst the fish is held in a net. The process takes seconds and researchers have already confirmed that it collects enough DNA for analysis.
“While swabbing appears to be less invasive than fin clipping, it still requires fish to be netted, held in the air and handled; procedures that could potentially cause stress,” Dr Norton continued. “Therefore, the potential of swabbing as a refinement to standard DNA collection by fin clipping remains untested.”
Dr Ioanna Katsiadaki, a principal investigator at Cefas and an expert in the assessment of fish welfare, will collaborate on the project and provide state-of-the-art facilities for the less-invasive measurement of stress hormones released naturally by fish into the water through their gills.
The project, 'Quantifying the potential of skin swabbing as a refinement for DNA sampling of laboratory fish', will be funded by the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research.
Image (C) University of Leicester



 The RCVS has announced a new version of its 1CPD mobile app, with enhanced features for veterinary surgeons and veterinary nurses to record their continuing professional development.
The RCVS has announced a new version of its 1CPD mobile app, with enhanced features for veterinary surgeons and veterinary nurses to record their continuing professional development.